Bronchitis
Bronchitis is a disease characterized by inflammation of the bronchi which carry air to your lungs. Being a fairly common condition, it begs the question, is bronchitis contagious? Since bronchitis is usually caused by an infectious agent, you would assume it would be contagious. However, bronchitis can be both contagious and non-contagious, depending on what brought the symptoms on. To glean a better understanding about this, you must first learn more about what causes bronchitis and what it actually is.
- What is Bronchitis?
- Symptoms of Bronchitis
- Causes of Bronchitis
- Is Bronchitis Contagious?
- What is the Contagious period for Bronchitis?
- Is Bronchitis Contagious in Children?
- How long is Bronchitis Contagious after taking Antibiotics?
- Who gets Bronchitis?
- How to prevent Bronchitis?
- Diagnosis
- Treatment for Bronchitis
- When to see a Doctor?
What is Bronchitis?
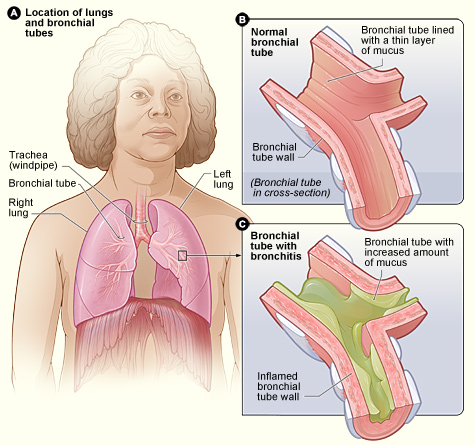
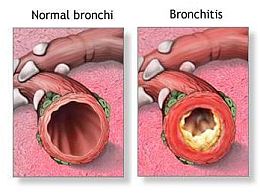
As already mentioned, bronchitis is the inflammation of the mucous lining of the bronchial tubes in your lungs. The inflammation, caused by swelling and redness, may be due to attack by an infectious agent. While it is true that most cases of bronchitis are brought on by the common cold, some more long lasting cases actually have very different causes. On the basis of duration of disease, Bronchitis is differentiated into chronic and acute bronchitis. This differentiation may also answer the question: “Is bronchitis contagious?”
Acute Bronchitis
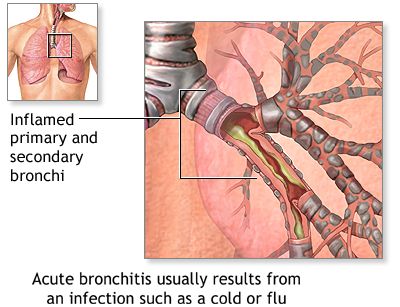
Acute bronchitis is caused by an upper respiratory tract infection. 90 % of the time, this infection is caused by viruses such as influenza virus or a rhinovirus. However, Acute bronchitis can also be caused by bacterial infections even though it is pretty rare. Identified easily due to the stereotypical mucous producing cough, Acute bronchitis usually follows a bout of flu. The cough is actually a defense mechanism of the body, as it propels the mucus away from the respiratory tubes where it is gathering. The narrowing of the airways due to the swelling also makes it difficult to breathe properly. Acute bronchitis is usually short lasting and non-recurring.
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is much more serious as compared to Acute bronchitis. It occurs as a result of continued irritation and swelling of the bronchial lining over a course of many years. This damage may be caused by a variety of environmental factors like air pollution. However it is most commonly found in people with prolonged exposure to cigarette smoke. Due to its long duration and recurrence it is actually a type of chronic obstructive disease. People with occupations like coal mining, textile manufacturing and livestock farming are also more susceptible to this disease. The cough is chronic and worse in the mornings. Constant inflammation obstructs the airways and causes wheezing and shortness of breath.
Symptoms of Bronchitis
Patients suffering from Bronchitis experience a variety of symptoms. Even though the causes of both diseases suffer greatly, acute bronchitis symptoms are actually quite similar to chronic bronchitis symptoms. The signs of bronchitis include:
- Sore throat
- Chest discomfort
- Runny nose
- Weakness
- Fever
- Shortness of breath
Wheezing - Persistent Cough that produces mucus – The mucus may be clear or green, depending on the seriousness of the infection. In patients suffering from chronic Bronchitis, the mucus may even be flecked with blood.
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
Causes of Bronchitis
As you may have understood from the description above, bronchitis can be caused by a variety of factors. Viral infections that affect the sinuses or the throat may spread lower into the respiratory tract and cause bronchitis. Some bacteria like Streptococcus Pneumoniae can also spread like this.
Other causes are environmental; they include any particle that can irritate the mucous lining of the respiratory tract on prolonged exposure. Toxic levels of nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide can also cause a lot of damage to bronchi. Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of chronic bronchitis as it releases a steady of stream of lung irritants and poisonous carbon monoxide into the bronchial tubes.
Patients already suffering from chronic bronchitis due to an environmental cause can also contract a viral or bacterial infection that can further distress their lungs. Asthmatic patients already have inflamed bronchi. They may also however, contract Asthmatic Bronchitis due to a viral infection or allergen.
Normal and inflamed bronchi
Is Bronchitis Contagious?
Now that you know more about the different types and causes of Bronchitis, you will understand why it is both contagious and non-contagious. As is obvious, Acute Bronchitis, cause by viral or bacterial infection is definitely contagious. When a person suffering from Acute bronchitis coughs or sneezes, they release millions of tiny droplets which contain the virus within them. These may be inhaled by a person standing nearby. They may also land on the surrounding objects, where they may survive for about a day. Hence anyone touching an object infected by the patient will not only contract the virus himself but also spread it around by touch other objects. Hence it is prudent to say that infectious Bronchitis is highly contagious.
On the other hand, chronic bronchitis is a disorder with very different causes. Since it is not due to an infectious agent, it cannot be transmitted to other people. Hence it is non-contagious.
What is the Contagious period for Bronchitis?
Many people are curious about how long the disease stays contagious. While it is necessary to stay careful and hygienic at all times, acute bronchitis is contagious as long as the symptoms persist. Whether you are on a treatment or not, your cough lingers for about 5 to 6 days, and until it stops your disease is still very much contagious.
Is Bronchitis Contagious in Children?
Bronchitis in children is very common. This is because children usually are not that careful when it comes to covering their mouths while coughing, or being careful about what they touch. Along with their habit of constantly putting things in their mouth or just touching them, another reason they are more susceptible is their weak immune system. As they grow up, their immune system becomes stronger and their body becomes more capable of fighting of infections. Therefore, Bronchitis caused by infectious agents is highly contagious in children.
How long is Bronchitis Contagious after taking Antibiotics?
If you’re wondering if taking antibiotics will reduce the contagiousness of bronchitis then you are wrong. Antibiotics work only in the case of bacterial bronchitis, and even then they must be given 5 to 6 days’ time to eradicate all the disease causing bacteria in your system. Hence it doesn’t make much of a difference to the level of contagiousness if you’re on antibiotics. Just take extra precautions until your symptoms completely disappear.
Who gets Bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis affects people of all ages, sizes and gender. As it is caused by a viral or bacterial infection, everyone is exposed to the risk of acute bronchitis. However children and the elderly are more susceptible to the disease; the former due to their lack of hygiene and the latter due to their weak immune system.
Chronic bronchitis affects people who have a habit of smoking cigarettes or work in cloth manufacturing factories, coal mines, metal industries and grain processing.
How to prevent Bronchitis?
To prevent contraction of acute bronchitis, you must be very careful with what you touch. Make sure you wash your hands before touching your mouth. If you are suffering from the disease, hydrate a lot and take loads of bed rest. Covering your mouth and nose with a handkerchief while coughing or sneezing is also effective in preventing its’ spread.
Chronic bronchitis can be prevented by giving up smoking if you have a habit of cigarette smoking. In other environmental cases if you do not have the option of changing your occupation, wearing a mask to cover your nose and mouth will help. Avoid second hand smoke and air pollution as best as you can.
Diagnosis
The doctor will diagnose your disease based on your signs and symptoms. He may also listen to your breath sounds through a stethoscope. Abnormal, coarse breathing sounds will confirm the diagnosis of bronchitis. Furthermore, he may carry out some tests like a Chest X-ray and Pulse Oximetry to rule out pneumonia or other Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases (COPD).
Treatment for Bronchitis
Treating bronchitis is more of a natural process. In cases of bacterial infection your doctor may prescribe antibiotics for bronchitis. However antibiotics are completely ineffective if you have viral bronchitis. Therefore, treatment of acute bronchitis is usually symptomatic, that is to alleviate the symptoms. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and cough syrups are usually prescribed. You may also be given some aspirin to relive the fever.
Having said all of this, most cases of acute bronchitis are relieved without treatment. It is actually better for your body if you use natural remedies for bronchitis. These include using a humidifier or taking steam to unclog the mucus in your system. This steam travels up and down your respiratory pathway and thus is very effective. Drinking herbal teas and honey in water helps in relieving your sore throat.
Chronic bronchitis is harder to treat. If the damage to your lungs is permanent, you may even need a lung transplant. However in most cases, removing the environmental factor or smoking habit that is causing the disease, leads to a rise in lung function. In any case you may be prescribed a variety of bronchodilators or corticosteroids by your doctor to help with your symptoms.

Young woman with bronchodilator
When to see a Doctor?
Even though dealing with Acute bronchitis is comparatively easy, you must contact your doctor at once if you go through any of the following things:
- A recurring cough, or a persistent cough
- Cough with dredges of blood
- High fever and shaking chills
- Low grade fever for more than 3 days
- Thick, green, foul-smelling mucus
- Chest pain or shortness of breath
Additionally, if you already suffer from a chronic heart or lung disease, you must seek immediate medical attention. Asthmatic patients may also confer with their doctor to get help dealing with the extra inflammation.
References:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0002078/
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21121518
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9004313
http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/brnchi/signs.html
http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Bronchitis/Pages/Causes.aspx
Spencer, S; Karner, C; Cates, CJ; Evans, DJ (2011). “Inhaled corticosteroids versus long acting beta(2)-agonists for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease”. Cochrane database of systematic reviews 12 (CD007033). doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007033.pub3. PMID 22161409.
Karner, C; Chong, J; Poole, P (2012). “Tiotropium versus placebo for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease”. Cochrane database of systematic reviews 7 (CD009285). doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009285.pub2. PMID 22786525.
Cohen, Jonathan; Powderly, William (2004). Infectious Diseases, 2nd ed. Mosby (Elsevier). Chapter 33: Bronchitis, Bronchiectasis, and Cystic Fibrosis. ISBN 0323025730.
Albert, RH (December 2010). “Diagnosis and treatment of acute bronchitis”. American Family Physician 82 (11): 1345–1350. PMID 21121518.

 Facebook
Facebook  Twitter
Twitter  RSS
RSS